Pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection that affects the lungs, causing inflammation in the air sacs (alveoli). Recognizing pneumonia symptoms early can help in getting timely treatment and preventing complications. This guide covers the early signs of pneumonia, severe symptoms requiring emergency care, causes, risk factors, and effective treatment options.
Must Check: Insomnia Symptoms
Pneumonia Symptoms: Signs to Watch For
Pneumonia symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on the cause, age, and overall health of the patient. Some people may experience flu-like symptoms that gradually worsen, while others may develop sudden, severe illness.
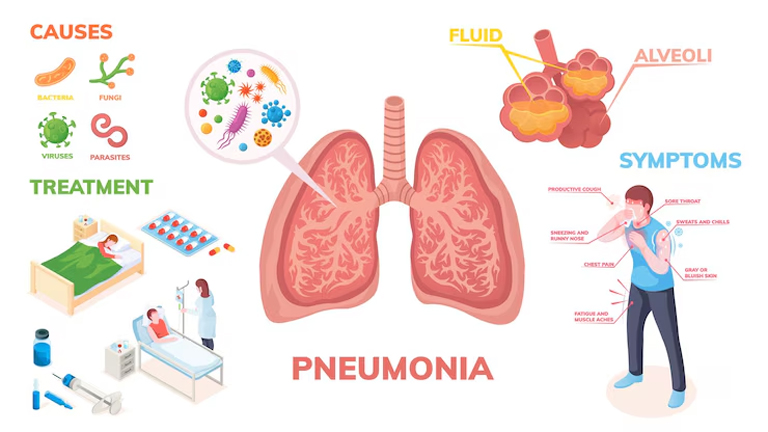
The most common pneumonia symptoms include:
-
Cough (may produce green, yellow, or bloody mucus)
-
Fever, sweating, and chills
-
Shortness of breath (especially during physical activity)
-
Chest pain (sharp or stabbing, worsens with deep breaths or coughing)
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Loss of appetite
-
Confusion (more common in older adults)
Symptoms can vary based on the type of pneumonia:
-
Bacterial pneumonia – High fever, productive cough, rapid breathing.
-
Viral pneumonia – Dry cough, headache, muscle pain, fatigue.
-
Walking pneumonia (Atypical pneumonia) – Mild symptoms, often mistaken for a cold.
Common Symptoms of Pneumonia
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the most frequent signs of pneumonia:
1. Persistent Cough
A cough that produces thick mucus (sputum) is a hallmark symptom. The mucus may be discolored due to infection.
2. Fever & Chills
High fever (above 101°F or 38.5°C) with shaking chills indicates a bacterial infection.
3. Breathing Difficulties
Shortness of breath, rapid breathing (tachypnea), and wheezing occur as lung function declines.
4. Chest Pain
Inflammation in the lungs causes sharp chest pain, especially when coughing or inhaling deeply.
5. Fatigue & Weakness
The body fights infection by diverting energy, leading to extreme tiredness.
6. Nausea, Vomiting, or Diarrhea
More common in children and those with viral pneumonia.
7. Bluish Lips or Nails (Cyanosis)
A sign of low oxygen levels, requiring immediate medical attention.
Severe Symptoms (When to Seek Help)
Some pneumonia symptoms indicate a medical emergency. Seek urgent care if you or a loved one experiences:
✔ High fever (above 102°F or 39°C)
✔ Difficulty breathing or gasping for air
✔ Confusion or disorientation (common in elderly patients)
✔ Persistent chest pain
✔ Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
✔ Blue-tinged lips or fingertips (oxygen deprivation)
High-risk groups (infants, elderly, immunocompromised individuals) should seek medical help at the first sign of pneumonia.
Causes & Risk Factors
Pneumonia develops when germs (bacteria, viruses, fungi) infect the lungs. The most common causes include:
1. Bacterial Pneumonia
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae (most common cause)
-
Haemophilus influenzae
-
Legionella pneumophila (Legionnaires’ disease)
2. Viral Pneumonia
-
Influenza (flu virus)
-
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
-
COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)
3. Fungal Pneumonia
-
Pneumocystis pneumonia (common in HIV/AIDS patients)
-
Histoplasmosis (from soil or bird droppings)
Risk Factors Increasing Pneumonia Chances
-
Age (infants & adults over 65)
-
Chronic diseases (asthma, COPD, diabetes, heart disease)
-
Smoking (damages lung defenses)
-
Weakened immune system (HIV, chemotherapy)
-
Hospitalization (ventilator-associated pneumonia)
Pneumonia Symptoms, Causes & Treatments at a Glance
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Symptoms | – Persistent cough (with mucus) – Fever & chills – Shortness of breath – Chest pain – Fatigue & weakness |
| Severe Symptoms | – High fever (>102°F/39°C) – Confusion (especially in elderly) – Bluish lips/nails – Difficulty breathing |
| Main Causes | Bacterial: Streptococcus pneumoniae Viral: Flu, RSV, COVID-19 Fungal: Pneumocystis (in immunocompromised) |
| Risk Factors | – Age (infants/elderly) – Smoking – Chronic diseases (COPD, diabetes) – Weakened immune system |
| Treatments | Bacterial: Antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin) Viral: Antivirals (e.g., oseltamivir) Severe Cases: Oxygen therapy, hospitalization |
| Prevention | – Vaccines (pneumococcal, flu) – Hand hygiene – Quit smoking – Boost immunity (diet/exercise) |
Treatment & Prevention
Medical Treatments for Pneumonia
-
Antibiotics (for bacterial pneumonia, e.g., amoxicillin, azithromycin)
-
Antiviral drugs (for flu-related pneumonia, e.g., oseltamivir)
-
Antifungal medications (for fungal infections)
-
Oxygen therapy (for severe cases with low oxygen levels)
-
IV fluids & hospitalization (if dehydration or breathing difficulties occur)
Home Remedies & Recovery Tips
-
Stay hydrated (water, herbal teas, broths)
-
Rest to help the immune system fight infection
-
Use a humidifier to ease breathing
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers (ibuprofen, acetaminophen for fever)
-
Avoid smoking & air pollutants
Preventing Pneumonia
✅ Get vaccinated (Pneumococcal vaccine, flu shot, COVID-19 vaccine)
✅ Practice good hygiene (wash hands frequently)
✅ Quit smoking (improves lung health)
✅ Strengthen immunity (balanced diet, regular exercise)
✅ Avoid close contact with sick individuals
Final Thoughts
Recognizing pneumonia symptoms early can prevent severe complications like sepsis or lung abscess. If you experience persistent cough, fever, or breathing troubles, consult a doctor immediately. With proper treatment—whether antibiotics, antivirals, or supportive care—most people recover fully.
Prevention is key, especially for high-risk individuals. Vaccinations, healthy habits, and prompt medical attention can significantly reduce pneumonia risks. Stay informed and protect your lung health!
FAQs About Pneumonia Symptoms
Q: How long do pneumonia symptoms last?
A: Mild cases improve in 1-2 weeks, while severe pneumonia may take 4-6 weeks.
Q: Can pneumonia go away on its own?
A: Viral pneumonia may resolve without treatment, but bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics.
Q: Is pneumonia contagious?
A: Yes, bacterial and viral pneumonia can spread through droplets from coughing/sneezing.
Q: What’s the difference between pneumonia and bronchitis?
A: Bronchitis affects the airways, while pneumonia infects the lung’s air sacs, causing more severe symptoms.
By understanding pneumonia symptoms and treatments, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your respiratory health. If in doubt, always seek medical advice.