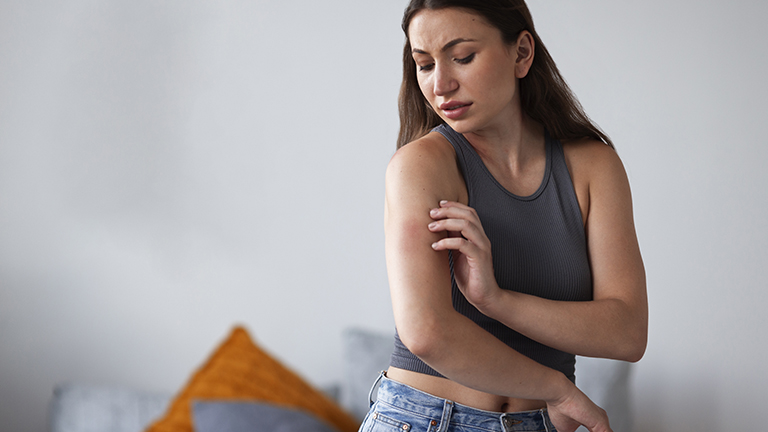
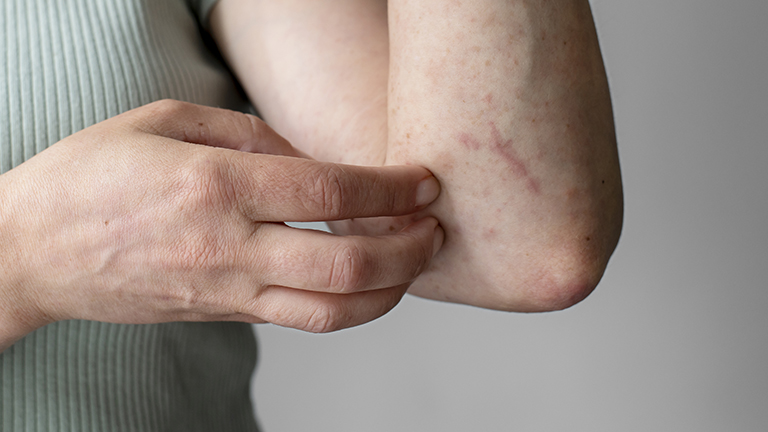
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin, leading to intense itching, redness, and rashes. Affecting people of all ages, scabies can spread rapidly through close contact or shared personal items like clothing and bedding. Prompt and effective treatment is essential to eliminate the mites, relieve discomfort, and prevent reinfection. This comprehensive guide covers proven prescription medications, natural remedies, step-by-step application techniques, preventive measures, and expert tips. Whether you are an adult, parent, or caregiver, understanding proper <strong>treatment for scabies</strong> is crucial for fast relief and long-term protection.
Treatment for Scabies Table of Contents
- Understanding Scabies
- Effective Treatments for Scabies
- Step-by-Step Guide to Treating Scabies
- Preventing Scabies Reinfection
- Special Cases in Scabies Treatment
- Lifestyle and Home Care Tips
- Expert Tips for Fast Recovery
- Case Examples
- Frequently Asked Questions About Scabies Treatment
Understanding Scabies
What is Scabies?
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. The microscopic mites burrow into the skin, triggering intense itching, redness, and small rashes. It affects people of all ages and spreads rapidly through direct skin contact or contaminated personal items.
Causes of Scabies Infection
Scabies spreads primarily via:
- Prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person
- Sharing towels, clothing, bedding, or furniture
- Living in crowded environments
- Weakened immune systems increasing susceptibility
Symptoms in Adults, Children, and Infants
Symptoms vary by age and severity:
- Itching that worsens at night
- Reddish or pink rash, often in skin folds (between fingers, wrists, elbows, waist)
- Blisters or pustules in severe cases
- In infants, rash can appear on the head, face, palms, and soles
- Thick crusts in crusted scabies, a severe form
Effective Treatments for Scabies
Prescription Medications for Scabies
Medical treatments are the most reliable way to eliminate scabies mites:
- Permethrin 5% cream: Topical application from neck to toes, left for 8–14 hours, effective for adults and children over two months old.
- Oral Ivermectin: Used for severe or crusted scabies, often in combination with topical creams. Dosage based on body weight.
- Crotamiton 10% cream: Alternative for adults unable to use permethrin. Apply as directed by a physician.
Over-the-Counter Options
OTC treatments can alleviate symptoms but may not kill mites:
- Antihistamines to reduce itching
- Calamine lotion for soothing irritation
- Topical hydrocortisone for inflammation relief
Natural and Home Remedies
Complementary remedies include:
- Tea tree oil: Contains terpinen-4-ol, effective against scabies mites. Dilute before application to avoid skin irritation.
- Neem oil: Traditional remedy with anti-inflammatory properties.
- Aloe vera gel: Soothes irritated skin after treatment.
Step-by-Step Guide to Treating Scabies
How to Apply Scabies Creams Correctly
- Shower and pat dry before application.
- Apply cream evenly from neck to toes, including under nails and scalp if affected.
- Leave cream on for recommended duration (8–14 hours).
- Shower thoroughly after treatment.
Dosage and Duration for Oral Medications
Oral ivermectin dosage is typically weight-based. Repeat dose after 7–14 days if required. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult a doctor before using oral medications.
Reducing Itching and Skin Irritation
- Use antihistamines or soothing lotions
- Avoid scratching to prevent secondary infections
- Keep nails short and clean
Preventing Scabies Reinfection
Cleaning Clothes, Bedding, and Personal Items
Wash all clothes, bedding, and towels in hot water and dry on high heat. Seal items that cannot be washed in plastic bags for at least 72 hours.
Avoiding Close Contact During Infection
Limit physical contact with others until treatment is complete. Household members should be monitored and treated if necessary.
Monitoring Family Members
Scabies spreads easily among household members. Watch for signs of rash or itching and treat promptly to prevent reinfestation.
Special Cases in Scabies Treatment
Pediatric Scabies Care
Children require milder treatments. Permethrin cream is safe for children over two months old. Consult a pediatrician for severe or persistent cases.
Crusted Scabies Treatment
Crusted scabies requires intensive therapy: oral ivermectin combined with topical creams. Frequent monitoring and repeated treatments are often necessary.
Pregnancy and Scabies
Permethrin cream is the first-line treatment during pregnancy. Oral ivermectin is generally avoided unless necessary under strict medical supervision.
Lifestyle and Home Care Tips
Maintaining Skin Hygiene
Daily showers and gentle cleansing can reduce itching and inflammation. Avoid harsh soaps that dry the skin.
Boosting Immunity
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps the body fight infections and recover faster from scabies infestations.
Clothing and Bedding Practices
Wear clean, loose-fitting clothes. Wash bedding regularly during and after treatment to prevent reinfection.
Environmental Cleanliness
Vacuum carpets, furniture, and rugs to remove stray mites. Encourage family members to follow the same hygiene practices.
Expert Tips for Fast Recovery
- Apply treatment cream at night to maximize efficacy.
- Treat all household members simultaneously to avoid reinfection.
- Keep track of symptoms and follow up with a healthcare provider if itching persists beyond four weeks.
- Avoid scratching to prevent secondary bacterial infections.
- Use moisturizers after treatment to reduce skin dryness and irritation.
Case Examples
Adult Male with Severe Itching
A 35-year-old male developed intense itching after visiting a crowded gym. Prescription permethrin cream was applied, and close contacts were treated. Symptoms resolved within 10 days.
Pediatric Case
A 4-year-old child showed red rashes and itching. Permethrin cream safe for children was applied, and bedding washed thoroughly. The child recovered completely within 2 weeks.
Crusted Scabies in Elderly Patient
An 80-year-old nursing home resident had thick crusted scabies. Intensive treatment with oral ivermectin and topical creams over 4 weeks eliminated the infestation. Staff were trained on hygiene practices to prevent further outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions About Scabies Treatment
How long does scabies treatment take?
Most cases clear within 1–2 weeks after treatment. Itching may persist for up to 4 weeks.
Can scabies come back after treatment?
Yes, reinfection is possible if contacts are untreated or hygiene measures are inadequate.
Are home remedies enough to cure scabies?
Home remedies can soothe symptoms but cannot eradicate mites. Prescription treatments are essential.
Is scabies contagious?
Yes, scabies spreads easily via skin-to-skin contact and shared personal items.
Can scabies affect pets?
Human scabies mites are species-specific. Pets have their own type of mites and require veterinary care.
Can scabies be prevented naturally?
Maintaining hygiene, washing bedding regularly, and avoiding contact with infected individuals can reduce risk, but complete prevention requires treatment if exposed.
Can scabies cause long-term skin damage?
Itching and scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections, but proper treatment prevents permanent skin damage.
When should I see a doctor?
If itching persists beyond two weeks after treatment, or if there are severe rashes, blisters, or crusted scabies, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Conclusion
Effective treatment for scabies combines prescription medications, hygiene measures, and careful monitoring. By following step-by-step instructions, applying creams properly, treating all household members, and maintaining environmental cleanliness, scabies can be eliminated quickly. Awareness, early intervention, and preventive measures are key to controlling scabies outbreaks across the globe.