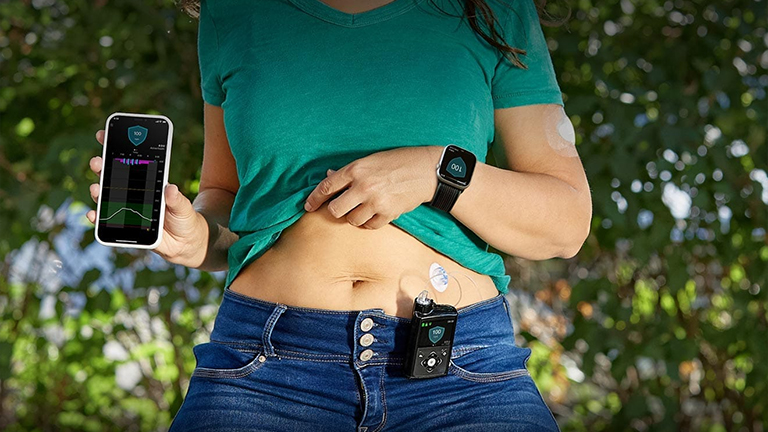
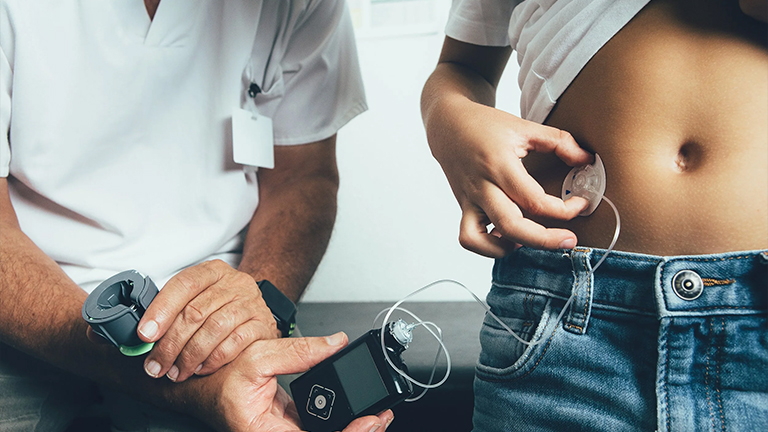
Managing diabetes effectively requires precise and consistent insulin delivery, which can be challenging with traditional injections. Insulin pump therapy has emerged as a revolutionary solution, offering continuous insulin infusion that closely mimics the natural function of the pancreas. This advanced technology provides patients with greater control over blood sugar levels, reduces the risk of hypoglycemia, and allows more flexibility in daily routines, meals, and physical activity.
Modern insulin pumps often integrate with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and smart systems, creating semi-automated or fully automated insulin delivery solutions, sometimes referred to as artificial pancreas systems. These innovations not only improve glucose management but also enhance patient quality of life by reducing the burden of frequent injections and constant blood sugar monitoring.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything about insulin pump therapy, including its benefits, risks, device options, daily management strategies, and future developments. Whether you are a type 1 diabetes patient, a type 2 patient requiring intensive insulin, or someone seeking more lifestyle flexibility, this article provides the insights needed to make informed decisions about your diabetes care.
What is an Insulin Pump?
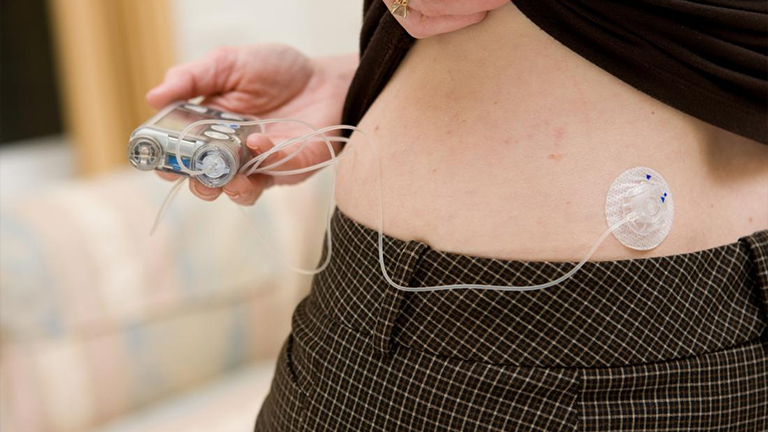
An insulin pump is a small, computerised medical device designed to deliver insulin continuously to individuals with diabetes. Unlike traditional insulin injections, which are given multiple times a day, an insulin pump provides a steady basal insulin supply throughout the day and night, closely mimicking the natural function of the pancreas.
Patients can also program bolus doses to manage blood sugar spikes caused by meals or high glucose levels. The pump is connected to the body via a thin tube or cannula inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen, thigh, or arm.
Modern insulin pumps often integrate with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), allowing real-time glucose tracking and automated insulin adjustments. This combination improves blood sugar control, reduces hypoglycemia risk, and offers greater lifestyle flexibility compared to multiple daily injections.
Overall, insulin pumps provide a convenient, precise, and flexible approach to diabetes management, improving both health outcomes and quality of life for patients.
History and Evolution of Insulin Pumps
The first insulin pumps were developed in the late 1970s and were relatively large and cumbersome. Over the decades, technological advancements have led to compact, smart insulin pumps with features such as:
- Integration with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)
- Automated insulin delivery adjustments
- Smartphone connectivity for remote monitoring
- Alarms for low or high blood sugar levels
These innovations have transformed diabetes care, improving blood sugar control and patient quality of life.
How Insulin Pump Therapy Works
Continuous Insulin Delivery Explained
Insulin pumps provide a steady infusion of rapid-acting insulin throughout the day and night. This basal insulin keeps glucose levels within a target range between meals and during sleep. Patients can also administer bolus doses to cover carbohydrate intake from meals or correct high blood sugar.
This method of insulin delivery mimics the pancreas more closely than injections, reducing the risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Integration with Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Modern insulin pumps often work in tandem with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), which track blood sugar levels in real time. The CGM sensor, inserted under the skin, measures glucose continuously and sends the data to the pump.
This integration allows the pump to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on current glucose readings, reducing the risk of highs and lows. Some advanced systems form a semi-closed loop, often called an artificial pancreas, where insulin dosing is dynamically regulated with minimal manual input.
By combining CGMs with insulin pumps, patients achieve better blood sugar control, fewer hypoglycemic episodes, and more freedom in daily activities, making diabetes management safer and more convenient.
Benefits of Insulin Pump Therapy
Improved Blood Sugar Control
One of the primary benefits of insulin pump therapy is its ability to provide precise and consistent blood sugar management. By delivering a continuous basal dose of insulin and allowing for customise able bolus doses at mealtimes, pumps help maintain glucose levels within a target range more effectively than multiple daily injections.
This precise insulin delivery reduces fluctuations in blood sugar, minimising both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Studies have shown that patients using insulin pumps often achieve lower HbA1c levels, improved post-meal glucose control, and decreased long-term complications.
For individuals with type 1 diabetes or those requiring intensive insulin therapy, this enhanced control significantly improves daily well being, energy levels, and overall quality of life.
Flexible Lifestyle and Meal Management
Insulin pump therapy allows patients to manage their diabetes with greater flexibility, adjusting insulin doses based on meal timing, carbohydrate intake, and daily activities. Unlike multiple daily injections, pumps enable on-demand bolus delivery for meals and customise able basal rates for exercise or stress, helping maintain stable blood sugar levels. This adaptability supports a more normal lifestyle, reducing dietary restrictions and allowing individuals to eat, exercise, and travel with confidence while effectively controlling glucose levels.
Reduced Risk of Hypoglycemia
Insulin pump therapy helps significantly reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar levels. By providing a continuous basal insulin supply and allowing precise bolus adjustments, pumps maintain more stable glucose levels throughout the day and night.
When combined with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), the pump can alert users to falling glucose levels and even automatically adjust insulin delivery to prevent hypoglycemia. This real-time monitoring and responsive insulin management make diabetes care safer and more reliable, minimising sudden low blood sugar episodes and improving overall patient confidence and well being.
Enhanced Patient Satisfaction
Insulin pump therapy often leads to higher patient satisfaction compared to traditional insulin injections. The convenience of continuous insulin delivery, combined with the ability to adjust doses for meals, exercise, or stress, reduces the burden of frequent injections and strict schedules.
Patients also report feeling more in control of their diabetes management, with fewer blood sugar fluctuations and greater freedom in daily life. Integration with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) further enhances confidence by providing real-time glucose data and alerts. Overall, insulin pumps improve both quality of life and long-term health outcomes, making them a preferred choice for many individuals managing diabetes.
Who Should Consider Insulin Pump Therapy?
Type 1 Diabetes Patients
Insulin pump therapy is especially beneficial for individuals with type 1 diabetes, who require continuous insulin due to the body’s inability to produce it naturally. Pumps provide a steady basal insulin supply while allowing precise bolus doses to manage blood sugar spikes from meals or high glucose levels.
This method closely mimics the pancreas’s natural function, helping maintain stable blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications. For type 1 diabetes patients, insulin pumps offer greater flexibility, improved glucose control, and a more manageable daily routine compared to multiple daily injections.
Type 2 Diabetes Cases Requiring Intensive Insulin
While most type 2 diabetes patients manage their condition with oral medications or occasional insulin injections, some require intensive insulin therapy due to inadequate glucose control. For these individuals, insulin pump therapy can provide a more precise and consistent insulin delivery compared to multiple daily injections.
Pumps allow customise able basal and bolus doses to address fluctuating blood sugar levels caused by meals, activity, or stress. By improving glycemic control and reducing glucose variability, insulin pumps help type 2 diabetes patients minimise complications, prevent hypoglycemia, and achieve better overall management of their condition.
Patients Seeking Better Lifestyle Flexibility
Insulin pump therapy is ideal for patients who desire greater freedom and flexibility in their daily routines. Unlike multiple daily injections, pumps allow users to adjust insulin delivery based on meals, exercise, travel, or irregular schedules, providing more control over blood sugar levels.
This flexibility helps patients maintain a more balanced lifestyle, reducing stress around meal timing and insulin administration. For individuals with active or unpredictable routines, insulin pumps make diabetes management more convenient, less intrusive, and better suited to modern life, while still ensuring effective glucose control.
Risks and Challenges
Possible Side Effects
While insulin pump therapy is generally safe, some patients may experience side effects or complications. Common issues include skin irritation, redness, or infection at the insertion site if the cannula is not changed regularly.
Other risks involve pump malfunctions or insulin delivery interruptions, which can lead to hyperglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) if not addressed promptly. Some users may also experience site discomfort, bruising, or allergic reactions to the adhesive.
Proper site rotation, hygiene, and regular device maintenance, along with patient education, are essential to minimise these risks and ensure safe, effective insulin pump use.
While generally safe, insulin pump therapy may have some risks, including:
- Skin irritation at the insertion site
- Infection if the cannula is not changed regularly
- Diabetic ketoacidosis if the pump malfunctions or insulin delivery is interrupted
Cost and Insurance Considerations
Insulin pump therapy offers significant benefits for diabetes management but comes with substantial costs, which can vary based on insurance coverage and geographic location.
Out-of-Pocket Costs Without Insurance
Without insurance, the expenses associated with insulin pumps can be considerable:
- Initial Pump Cost: Typically ranges from $6,000 to $8,500 for the device itself. ProMed DME
- Annual Supplies: Including infusion sets, reservoirs, and other consumables, costs can range from $1,500 to $6,000 per year. ProMed DME
Insurance Coverage
Insurance plans, including Medicare, often cover a portion of the costs:
- Medicare Part B: Covers 80% of the approved cost for insulin pumps and related durable medical equipment (DME) supplies after a deductible is met. Solace
- Private Insurance: Coverage varies widely. Some plans may cover the full cost, while others might require co-pays or deductibles. It’s essential to review individual insurance policies for specific details.
Additional Considerations
- Prior Authorisation: Many insurance companies require prior authorisation before approving coverage for insulin pumps. Cigna
- Brand-Specific Coverage: Some insurers may have preferred brands or models, potentially limiting choices. Breakthrough T1D
- Financial Assistance Programs: Manufacturers often offer financial assistance or payment plans to help offset costs.
Given the potential financial burden, it’s advisable for patients to consult with their insurance providers and healthcare teams to understand coverage options and explore available financial assistance.
Device Malfunctions and Safety Tips
While insulin pumps are designed for reliability, device malfunctions can occur and may affect insulin delivery, potentially leading to hyperglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Common malfunctions include occluded cannulas, battery failure, software glitches, or pump alarms.
To ensure safe use, patients should follow these safety tips:
- Regularly Check the Device: Inspect the pump daily for alarms, error messages, or unusual operation.
- Rotate Infusion Sites: Change the cannula every 2–3 days to prevent blockages, infection, or skin irritation.
- Keep Backup Supplies: Always have extra insulin, syringes, and infusion sets in case of pump failure.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Frequently: Use finger-stick glucose checks or CGM readings, especially during travel or exercise.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to instructions for battery replacement, software updates, and device maintenance.
By following these precautions, patients can minimize risks, maintain consistent insulin delivery, and safely benefit from insulin pump therapy.
Comparing Insulin Pump vs. Injection Therapy
Convenience and Lifestyle Factors
Insulin pump therapy offers significant convenience compared to traditional insulin injections. By providing continuous basal insulin and on-demand bolus doses, pumps eliminate the need for multiple daily injections, allowing patients to manage their diabetes more easily.
The flexibility of insulin pumps supports irregular meal schedules, travel, and active lifestyles, as insulin delivery can be adjusted in real time. Patients can also participate in physical activities or social events without worrying about timing injections. This enhanced lifestyle flexibility not only improves daily comfort but also encourages better adherence to diabetes management, resulting in more stable blood sugar levels and improved overall quality of life.
Efficacy in Blood Sugar Control
Insulin pump therapy is highly effective in maintaining stable blood sugar levels compared to multiple daily injections. By delivering a continuous basal dose and allowing precise bolus adjustments for meals or high glucose readings, pumps help minimise hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Clinical studies have shown that patients using insulin pumps often achieve lower HbA1c levels, reduced glucose variability, and fewer severe hypoglycemic episodes. This improved efficacy is particularly beneficial for type 1 diabetes patients and those requiring intensive insulin therapy, supporting long-term health outcomes and better overall diabetes management.
Choosing the Right Insulin Pump
Selecting the appropriate insulin pump is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your diabetes management. With various models and features available, it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure the pump aligns with your lifestyle, medical needs, and personal preferences.
1. Insulin Delivery System
- Tubed Pumps: These pumps are connected to the body via a tube and an infusion set. They are often preferred by individuals who require higher insulin volumes or desire more flexibility in pump placement.
- Tubeless (Patch) Pumps: These pumps adhere directly to the skin without external tubing, offering a more discreet option. They are suitable for active individuals or those seeking a less obtrusive device.
2. Integration with Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Many modern insulin pumps integrate with CGMs, allowing for real-time glucose monitoring and automated insulin adjustments. This integration can help maintain blood sugar levels within a target range and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
3. Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems
Some insulin pumps feature hybrid closed-loop systems, which automatically adjust insulin delivery based on CGM data. These systems aim to mimic the body’s natural insulin release, providing more consistent blood sugar control.
4. Reservoir Capacity
Consider the pump’s reservoir size, especially if you have higher insulin requirements. A larger reservoir may reduce the frequency of refills, offering greater convenience.
5. Bolus and Basal Rate Flexibility
Evaluate the pump’s ability to deliver precise bolus doses and multiple basal rates. This flexibility is crucial for tailoring insulin delivery to your specific needs, such as varying activity levels or meal timings.
6. Screen Size and User Interface
A clear, easy-to-read screen and intuitive user interface are vital for effective pump management. Ensure the pump’s display is legible and that the navigation aligns with your preferences.
7. Waterproof or Water-Resistant Features
If you engage in activities like swimming or showering, consider a pump with waterproof or water-resistant capabilities to prevent damage.
8. Remote Control Capabilities
Some pumps offer remote control features, allowing adjustments without direct interaction with the device. This can be beneficial for discreet insulin delivery.
9. Insurance Coverage and Cost
Insurance plans vary in coverage for insulin pumps. Verify with your provider which models are covered and understand any associated costs, including co payments and deductibles.
10. Support and Training
Choose a pump that offers comprehensive support and training resources. Access to educational materials and customer service can facilitate a smoother transition to pump therapy.
Selecting the right insulin pump involves assessing your medical needs, lifestyle, and preferences. Consulting with your healthcare provider can provide personalised guidance to ensure optimal diabetes management.
For more detailed information on insulin pump selection, consider visiting reputable sources such as the American Diabetes Association and danatech.
Brand and Model Comparisons
When selecting an insulin pump, it’s essential to consider various factors such as device type, integration with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), system features, and user preferences. Here’s a comparative overview of some leading insulin pumps available in 2024:
1. Medtronic MiniMed 780G
- Type: Tubed
- CGM Integration: Guardian 4
- Closed-Loop System: Hybrid
- Features: Auto-correction boluses every 5 minutes, adjustable target glucose levels (100, 110, or 120 mg/dL), and predictive low glucose suspend.
- Ideal For: Users seeking a system with frequent insulin adjustments and customise able target glucose levels.
2. Tandem t:slim X2 with Control-IQ
- Type: Tubed
- CGM Integration: Dexcom G6
- Closed-Loop System: Hybrid
- Features: Auto-correction boluses every hour, adjustable target glucose range (112.5–160 mg/dL), and integration with Dexcom CGM for real-time glucose monitoring.
- Ideal For: Individuals preferring a system with less frequent insulin adjustments and a broader target glucose range.
3. Insulet Omnipod 5
- Type: Tubeless (Patch)
- CGM Integration: Dexcom G6
- Closed-Loop System: Hybrid
- Features: Pod-based insulin delivery without tubing, real-time glucose monitoring via Dexcom G6, and automated insulin adjustments.
- Ideal For: Users desiring a discreet, tubeless insulin delivery system with seamless CGM integration.
4. Beta Bionics iLet
- Type: Tubed
- CGM Integration: Dexcom G6
- Closed-Loop System: Hybrid
- Features: Automated insulin delivery with minimal user input, designed to simplify diabetes management.
- Ideal For: Individuals seeking a hands-off approach to insulin delivery with minimal manual adjustments.
5. Sequel twiist
- Type: Tubeless (Patch)
- CGM Integration: CamAPS
- Closed-Loop System: Hybrid
- Features: Smartphone-controlled insulin delivery, integration with CamAPS for automated insulin adjustments, and discreet pod-based system.
- Ideal For: Tech-savvy users preferring smartphone-based control and integration with CamAPS for automated insulin delivery.
Comparison Table:
| Model | Type | CGM Integration | Closed-Loop System | Auto-Correction | Ideal For |
| MiniMed 780G | Tubed | Guardian 4 | Hybrid | Every 5 minutes | Frequent insulin adjustments, customise able targets |
| t:slim X2 with Control-IQ | Tubed | Dexcom G6 | Hybrid | Every hour | Broader target range, less frequent adjustments |
| Omnipod 5 | Tubeless (Patch) | Dexcom G6 | Hybrid | Automated | Discreet, tubeless system |
| Beta Bionics iLet | Tubed | Dexcom G6 | Hybrid | Minimal input | Hands-off insulin delivery |
| Sequel twiist | Tubeless (Patch) | CamAPS | Hybrid | Smartphone-controlled | Smartphone-based control, CamAPS integration |
Note: The information provided is based on available data as of 2024. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Daily Management and Best Practices
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common problems include cannula dislodgement, occlusions, or pump alarms. Regular site rotation and proper insertion technique help prevent complications.
Tips for Beginners
- Keep a log of glucose readings and insulin doses
- Start with short basal adjustments and gradually optimise
- Stay in regular contact with a diabetes care team
Integrating Diet and Exercise
Insulin pump therapy allows patients to adjust insulin doses based on carbohydrate intake and physical activity, promoting a balanced lifestyle while maintaining blood sugar control.
Future of Insulin Pump Therapy
Artificial Pancreas and Smart Pumps
Emerging technologies aim to create fully automated insulin delivery systems, known as artificial pancreas systems. These devices integrate pumps, CGMs, and AI algorithms to maintain glucose levels with minimal manual input.
Innovations in Diabetes Technology
Continuous improvements in pump algorithms, remote monitoring, and wearable devices are making diabetes management more precise, less intrusive, and increasingly patient-friendly.
Conclusion & Expert Opinion
Insulin pump therapy represents a major advancement in diabetes care. By offering continuous insulin delivery, better blood sugar control, and lifestyle flexibility, it provides significant benefits over traditional injection methods.
Endocrinologists and diabetes experts recommend insulin pumps for patients struggling with frequent hypoglycemia, glucose variability, or lifestyle constraints. With ongoing innovations, insulin pump therapy is likely to become an even more integral part of diabetes management in the near future.