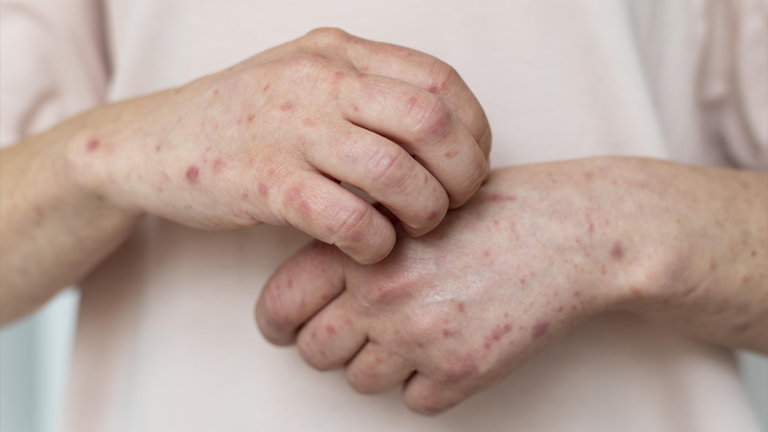
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects hair follicles, leading to inflammation, redness, and sometimes pus-filled bumps. It can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, including the scalp, face, arms, legs, and groin. While folliculitis is usually not serious, it can be uncomfortable and, in some cases, may lead to more severe infections if left untreated.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the different types of folliculitis, its causes, symptoms, treatment options (both medical and home remedies), and prevention tips to keep your skin healthy.
Must Check: Skin Cancer Causes
What Is Folliculitis? (Definition & Overview)
Folliculitis is the inflammation or infection of one or more hair follicles, the tiny openings from which hair grows. It often appears as small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles. The condition can be caused by bacterial, fungal, viral, or even inflammatory reactions to shaving, clogged pores, or excessive sweating.
Folliculitis can affect anyone, but some people are at higher risk, including:
-
Those with weakened immune systems
-
Individuals with acne or dermatitis
-
People who frequently shave or wax
-
Those who wear tight clothing that traps sweat and bacteria
While most cases are mild and resolve on their own, severe or recurring folliculitis may require medical treatment.
Types of Folliculitis (Bacterial, Fungal, Viral, Hot Tub Rash)
It can be classified into different types based on its cause:
1. Bacterial Folliculitis
The most common type, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus (staph bacteria). Symptoms include itchy, pus-filled bumps that may crust over. A subtype called “hot tub folliculitis” is caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa from poorly maintained hot tubs or pools.
2. Fungal Folliculitis
Caused by yeast or fungi, such as Malassezia or Candida. Common in people with dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) or those taking long-term antibiotics.
3. Viral Folliculitis
Often linked to the herpes simplex virus (HSV) or varicella-zoster virus (shingles). It may cause clusters of painful blisters.
4. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae (Razor Bumps)
Common in people with curly hair who shave frequently. Hair curls back into the skin, causing ingrown hairs and inflammation.
5. Gram-Negative Folliculitis
Occurs after long-term antibiotic use for acne, leading to bacterial resistance and new infections.
6. Eosinophilic Folliculitis
Seen in people with weakened immune systems (e.g., HIV/AIDS). Causes intense itching and recurring bumps.
Symptoms & How to Diagnose It (Visual Signs, Doctor Tests)
Common Symptoms of Folliculitis
-
Small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles
-
Clusters of itchy or tender bumps
-
Pus-filled blisters that may break open and crust over
-
Pain or burning sensation in affected areas
-
In severe cases, large swollen bumps or boils (furuncles)
Diagnosis
Most cases can be diagnosed by a visual examination. However, if the condition is severe or recurring, a doctor may:
-
Take a skin swab to identify bacteria or fungi
-
Perform a biopsy to rule out other skin conditions
-
Recommend blood tests if an immune disorder is suspected
Folliculitis vs. Acne: How to Tell the Difference
-
Folliculitis: Bumps are centered around hair follicles, often itchy or painful.
-
Acne: Includes blackheads, whiteheads, and deeper cysts, usually on the face, chest, and back.
Medical Treatments & Home Remedies (Antibiotics, OTC Creams, Natural Options)
Medical Treatments
-
Topical Antibiotics: Mupirocin or clindamycin for bacterial_folliculitis.
-
Oral Antibiotics: For severe cases (e.g., doxycycline, cephalexin).
-
Antifungal Creams/Shampoos: Ketoconazole for fungal folliculitis.
-
Steroid Creams: To reduce inflammation in chronic cases.
-
Laser Hair Removal: Helps prevent pseudofolliculitis barbae in recurring cases.
Home Remedies for Folliculitis
-
Warm Compress – Reduces swelling and promotes drainage.
-
Tea Tree Oil – Natural antibacterial properties (dilute before applying).
-
Apple Cider Vinegar – Helps balance skin pH (apply diluted).
-
Aloe Vera Gel – Soothes irritation and reduces redness.
-
Oatmeal Bath – Relieves itching and inflammation.
Note: Avoid squeezing or scratching folliculitis bumps to prevent scarring.
Prevention Tips (Hygiene, Shaving Tips, Avoiding Irritants)
To reduce the risk of folliculitis, follow these prevention strategies:
1. Proper Shaving Techniques
-
Use a clean, sharp razor.
-
Shave in the direction of hair growth.
-
Apply shaving gel to reduce friction.
-
Avoid shaving too close to prevent ingrown hairs.
2. Maintain Good Hygiene
-
Shower after sweating heavily.
-
Avoid sharing razors or towels.
-
Use antibacterial soap if prone to infections.
3. Wear Breathable Clothing
-
Choose loose, moisture-wicking fabrics to prevent sweat buildup.
4. Hot Tub & Pool Safety
-
Ensure proper chlorine levels in pools/hot tubs.
-
Shower immediately after swimming.
5. Avoid Skin Irritants
-
Skip heavy oils or greasy lotions that clog pores.
-
Use fragrance-free skincare products if sensitive.
Final Thoughts
Folliculitis is a common but manageable skin condition. While mild cases often clear up on their own, persistent or severe infections may require medical treatment. By following proper hygiene, shaving carefully, and using the right skincare products, you can prevent recurring flare-ups.
If you experience chronic_folliculitis or signs of infection (fever, spreading redness), consult a dermatologist for targeted treatment. With the right care, you can keep your skin healthy and irritation-free!
Have you dealt with folliculitis before? Share your experiences or questions in the comments!